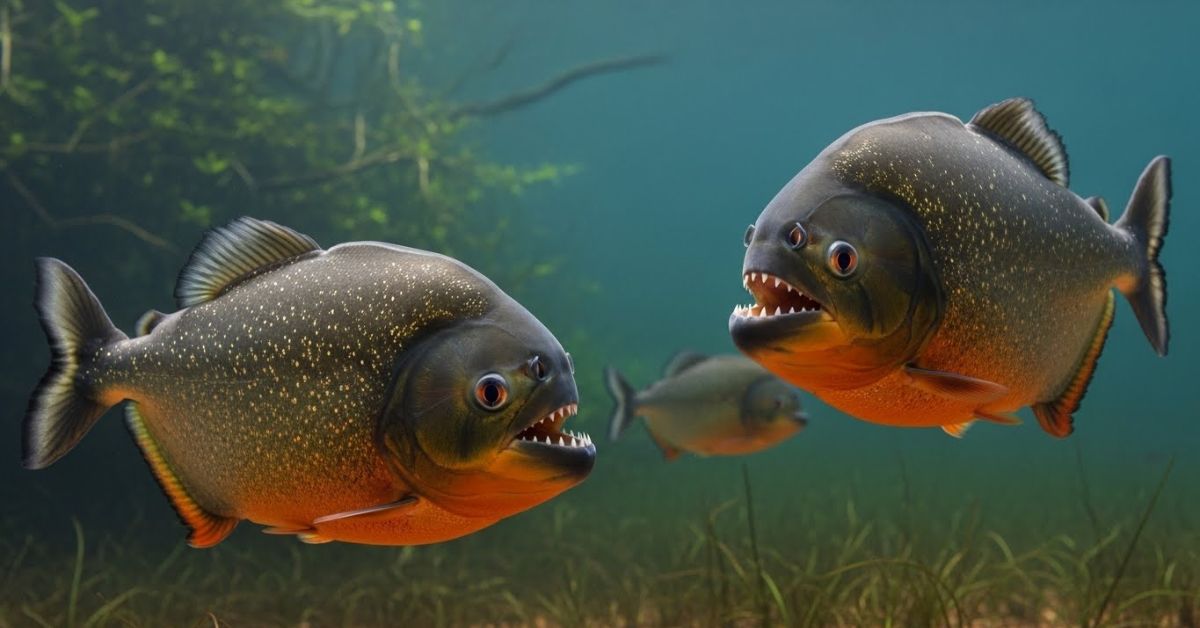
Deep within the lush waterways of South America lurks a fish that has captivated both fear and fascination in equal measure. The Piragnia, with its razor-sharp teeth and agile movements, has sparked awe and curiosity among scientists and locals alike. While many envision bloodthirsty schools tearing through the rivers, this creature’s reality is far more nuanced, blending remarkable adaptability with unique ecological roles. Understanding this fascinating fish not only sheds light on biodiversity but also highlights why it deserves both respect and protection in its natural habitat.
The presence of these fish in South American rivers demonstrates the balance of aquatic ecosystems, showcasing predator-prey interactions that are vital for maintaining healthy waterways. Its significance extends beyond folklore or fear; it is a living testament to nature’s complexity and the wonder of river life.
What is Piragnia?
Piragnia refers to a group of South American freshwater fish, often associated with the piranha. Known for their sharp teeth and powerful jaws, these species exhibit diverse behaviors that go beyond mere aggression.
While commonly feared, they play essential ecological roles as both predator and prey. Hunting strategies and feeding habits help maintain balance in rivers and lakes, preventing overpopulation of smaller species.
These fish thrive in varying habitats—from calm, slow-moving streams to riverbanks dense with vegetation—demonstrating adaptability that fascinates biologists. Each species contributes to the rich biodiversity of these aquatic ecosystems, making them a vital part of their environment.
Physical Characteristics and Habitat of Piragnia
This species is recognized for its robust, compact body and striking appearance, often growing up to 12 inches long. Its sharp teeth are functional tools for feeding, giving it a reputation as a formidable river dweller.
Coloration varies across types, with some displaying bright red or orange bellies while others sport darker, patterned bodies. This visual diversity supports camouflage and adaptability in complex aquatic environments.
Habitat preference includes warm rivers and lakes across South America. Vegetation-rich areas provide hiding spots and ambush points, while flooded forests during the rainy season create ideal breeding and feeding grounds. These environments ensure populations can thrive amid abundant food and shelter.
Diet and Hunting Habits of Piragnia
These fish are versatile feeders, preying on smaller fish, crustaceans, and insects. Their teeth are designed to slice efficiently, enabling both hunting and scavenging behaviors.
Many species hunt cooperatively in schools, surrounding and overwhelming prey with coordinated movements. This social hunting strategy maximizes success and ensures energy-efficient feeding.
A keen sense of smell allows them to locate food in murky waters, a vital adaptation in the dense rivers of South America. By balancing scavenging and active hunting, they remain resilient and adaptive predators within their ecosystems.
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Piragnia
Reproduction occurs during the rainy season when water levels rise, creating favorable conditions for eggs and fry. Females lay thousands of eggs in shallow, vegetated waters, while males actively guard nests against potential predators.
Once hatched, the young feed on small aquatic organisms and gradually expand their diet to include larger prey. Within months, they transform into capable predators, continuing the species’ life cycle, which typically spans up to five years in the wild.
Rapid growth ensures sustainable populations in dynamic river ecosystems. Proper habitat conditions and sufficient food supply are critical for their survival and development.
The Controversy Surrounding Piragnia
Media often sensationalizes these fish due to their reputation as fearsome predators. Misconceptions about their behavior have sparked debates among conservationists and anglers, with some advocating protective measures while others benefit from fishing tourism.
Exaggerated fears sometimes lead to habitat disruption or population decline. Illegal fishing for exotic pets or restaurant trade further threatens these species. Educating the public is key to fostering understanding and conservation while avoiding unnecessary vilification.
Conservation Efforts for Piragnia
Local and international organizations are working to protect habitats from deforestation, pollution, and unsustainable fishing. Awareness programs educate communities about the ecological importance of these fish.
River restoration projects create safer environments for populations to recover. Collaboration between scientists, local fishermen, and conservationists fosters long-term strategies to ensure that these species continue to thrive in natural habitats.
Protecting them is critical not only for maintaining healthy ecosystems but also for preserving biodiversity across South America’s waterways.
Conclusion
The Piragnia is integral to its ecosystem, helping maintain the balance of aquatic life in South America. Threats like habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing place populations at risk.
Educating communities about sustainable fishing practices and supporting conservation initiatives ensures that future generations can experience and study these remarkable fish. Every effort contributes to preserving the ecological heritage of South America’s rivers and the long-term survival of this fascinating species.
- Also Read QLCredit
FAQs
1. What exactly is a Piragnia?
Piragnia refers to piranha-like fish native to South America’s rivers and lakes. They are known for sharp teeth, diverse behaviors, and a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems.
2. Are all Piragnias dangerous to humans?
Most species primarily feed on smaller fish or plant matter. Attacks on humans are rare and usually occur only if they feel threatened.
3. How do you identify different types of Piragnia?
Different species can be distinguished by size, color patterns, and tooth shapes. Observing behavior and habitat also aids identification.
4. What do Piragnias eat?
Their diet includes insects, fruits, seeds from aquatic plants, smaller fish, and occasionally carrion.
5. Why is the conservation of Piragnias important?
Protecting these fish maintains healthy river ecosystems, supports local fisheries, and preserves biodiversity across South American waterways.
-
“Stay updated with the latest trends — visit True Realty Value today!”